A firewall monitors traffic entering and exiting the protected environment. It is possible to see the source and type of traffic that is coming into this environment with some firewalls as well. Rules are used to set up a firewall’s security settings. For a firewall’s ruleset to be effective, it must include an effective logging feature.
The firewall’s logging feature keeps track of how it handles different types of traffic. If an attack is detected, the logs can be used by a SIEM to help identify the source and destination IP addresses, protocols, and ports.
All firewalls have a logging feature that documents how the firewall handled various types of traffic while filtering Internet traffic. In addition to the IP addresses, ports, and protocols, these logs can provide valuable information. Using the Windows Firewall log file, you can also monitor TCP and UDP connections and packets that the firewall blocks.
What is Firewall Logging?
When it comes to a firewall, the most basic function is to prevent connections from being made to suspicious networks. Is it safe to trust a network by inspecting the source address of all connections, as well as the destination address and port?
Our source and destination addresses and ports are aggregated for convenience’s sake. An attempt to connect can be identified by this information, which is tracked by the firewall.
When it comes to making connections, this quality is similar to a set of rules that determine which connections are allowed and those that must be blocked.
By using an address that matches that of an already established connection, this source address can connect to its target via the allowed port. As a result, the network is open to traffic.
A successful logging feature should be added to a firewall ruleset in order to maximize its effectiveness.
The firewall’s logging feature reveals how it handles various types of traffic. Information like source and destination IP addresses, protocol versions, and port numbers can be gleaned from these logs.
Why Firewall Logging Is Important?
Here’s why firewall logging is important:
- To see whether newly added firewall rules are working properly to debug them or not.
- In order to determine if the Windows Firewall is causing application errors, firewall logging allows you to check for port openings that are either disabled or dynamic and to analyze packets that are either pushed or urgently dropped on the send path.
- With the Firewall logging feature, you can determine whether or not your network is experiencing any malicious activity. However, you must keep in mind that it does not provide enough information to identify or track down the source.
- If you notice that a particular IP address (or group of IP addresses) is repeatedly failing to enter your firewall and/or other high-profile systems, you may want to write a rule to drop all connections from that IP space.
- Outgoing connections from internal systems, such as Web servers, may indicate that your system is being used to attack computers on other networks.
Steps to Track Firewall Activity with the Windows Firewall Log
Here’s how you can easily track firewall activity with the Windows Firewall log:
The log file is disabled by default, so no data is recorded in the log file at all. Follow these simple steps to create a log file:
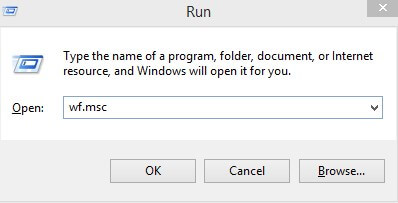
- First, open the Run dialog box by pressing Win + R together.
- In the Run dialogue box opens, type wf.msc and press Enter.
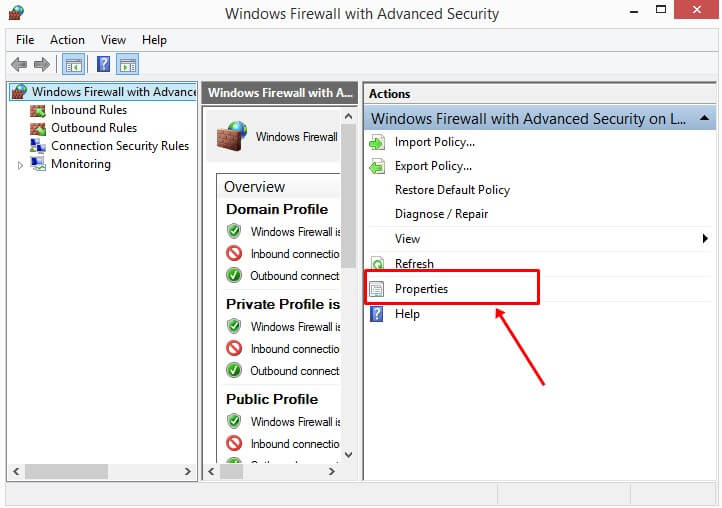
- Now, the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security screen will open.
- In that window, from the right side, click on Properties.
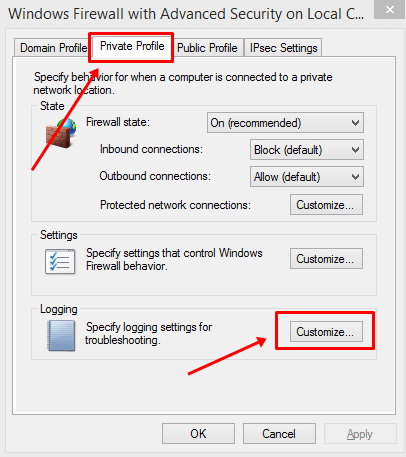
- Next, in the new dialog box, switch to the Private Profile tab. Click on Customize under the Logging section.
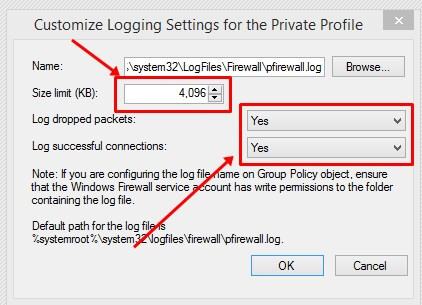
- In the new window that pops up, you can select the maximum log size and location, as well as whether or not you want to log only dropped packets or successful connections.
When a packet is rejected by Windows Firewall, it is known as a dropped packet. It is possible for an intruder to make a successful connection to your computer, but this does not necessarily mean that the intruder is successful to connect to your computer.
Windows Firewall, by default, logs all of its activity here:
%SystemRoot%\System32\LogFiles\Firewall\Pfirewall.log
However, it only saves the most recent 4 MB of data. In most production environments, this log will write to your hard disk on a regular basis, and changing the log file’s size limit (to log activity over a longer period of time) may have a performance impact.
Consequently, you should only enable logging when actively troubleshooting a problem, and then turn it off as soon as you’re done.
- Next, on the Public Profile tab, follow the same steps as you did for the Private Profile“. For both private and public network connections, you have now enabled the log.
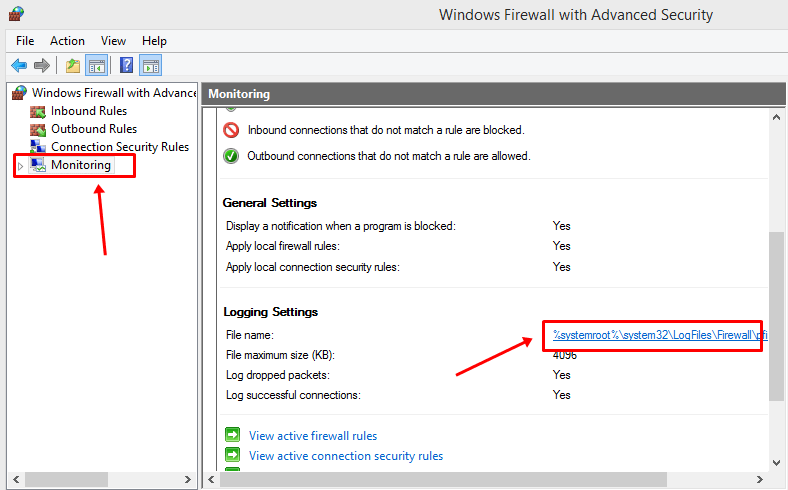
- After that, on the left panel, click on the Monitoring tab.
- Now click the file path next to File Name in the Details pane under Logging Settings.
- Notepad will now open the log file.
The log file will be saved in the W3C extended log format (.log), which you can examine in any text editor or import into a spreadsheet.
Since a single log file can contain thousands of text entries, you should disable word wrapping in Notepad to preserve column formatting. Further, if you open the log file in a spreadsheet, all of the fields will be organized into columns for easier analysis.